- HOME
- Medical Departments
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Treatment methods
Medical Departments
Cardiovascular Medicine
About diagnosis
We will treat patients using the safest and the most appropriate method according to each lesion.
We will consult with each patient to determine the safest and the most appropriate treatment method according to each lesion. Please ask any questions at any time.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is used to control symptoms. The most common drugs are antianginal drugs that dilate coronary arteries to increase the blood volume to the cardiac muscles, platelet aggregation inhibitors that improve blood flow, antiarrhythmic drugs that decrease the excitement of cardiac muscles and control the heart rate, and antihyperlipidemic drugs that promote the metabolism and excretion of blood cholesterol and reduce blood cholesterol concentrations. Existing drugs are not radical treatment.

Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a treatment method that allows the blood to flow again by dilating narrowed vessels using a balloon or stent (metal mesh) or cutting with a fast rotating cutter.
As PTCA is performed by inserting a catheter from the vessels of the wrist, elbow, or groin, as with its diagnosis, this procedure can minimize the burden on patients.
In addition, PTCT can be performed with a short hospitalization period, such as overnight or three days and two nights. In recent years, balloon therapy, stent therapy, and atherectomy have been used according to the solidity and degree of each lesion. We have been focusing on treatment in this field, and providing care with the latest technology and equipment.
Balloon therapy
Balloon therapy is a treatment method to dilate nearly clogged coronary arteries using a balloon to improve the blood flow. A catheter is inserted from the wrist, elbow, or groin to a nearly clogged lesion, and then the balloon is inflated. As balloon therapy is accompanied by only several days of hospitalization and a small amount of pain, it is the most common procedure used to treat ischemic heart disease.
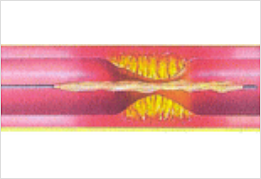
1. Advance a balloon along a dedicated wire to the target lesion.
2. Apply pressure to inflate the balloon.
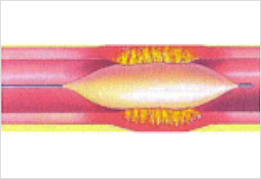
3. Reduce pressure to the balloon. The vessel is dilated, and the blood flow is improved.
Then remove the balloon, wire, and catheter immediately to complete the procedure.
Stent therapy
Some lesions cannot be adequately dilated even after balloon therapy. If these lesions remain untreated, they are highly likely to become clogged again. Therefore, a metal wire called a coronary artery stent is inserted into the lesion to reinforce the vessel wall and prevent re-clogging. The stent is placed using a method similar to that of balloon therapy.
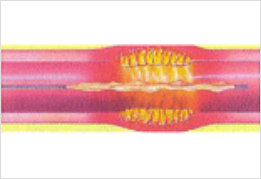
Advance a stent-equipped balloon system to the coronary artery and dilate it.
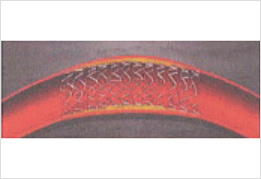
The stent is expanded and remains in the body to prevent the coronary artery from re-clogging.
Atherectomy
If the lesion is too hard to treat using balloon or stent therapy, atherectomy is useful to cut the lesion. This procedure can be performed only at hospitals meeting facility requirements. We use rotational atherectomy (Rotablator) to cut hard lesions that cannot be dilated with balloons. We choose safe and reliable treatment methods from various treatment options including Rotablator to treat each patient.
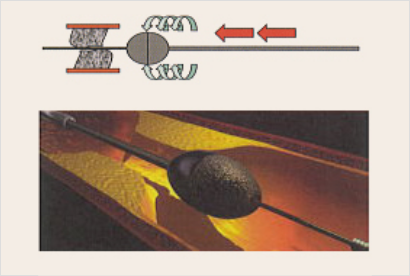
These are major treatment methods that we use. We will consult with each patient to determine the safest and the most appropriate treatment method according to each lesion. Please ask any questions at any time.
Treatment with CROSSER
What is CROSSER?
CROSSER is a device used to remove calcification from leg arteries with 20,000 vibrations per second to insert a catheter. With CROSSER, we can treat lesions that have been difficult to treat with a guidewire or catheter. Nagoya Kyoritsu Hospital introduced CROSSER for the first time in the Tokai and Hokuriku regions and pioneered the use of the device in Japan.
- Patients for whom a guidewire cannot be inserted
- Patients for whom a catheter cannot be inserted
- Patients with a highly calcified lesion
(Highly calcified lesions are often observed particularly in patients with dialysis.) - Patients with chronic total occlusion
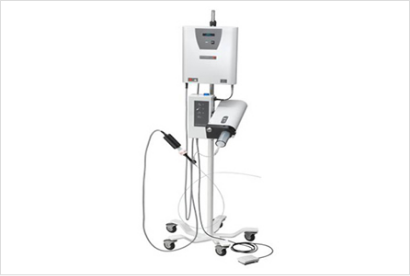
CROSSER enables the treatment of lesions that have been difficult to treat, shortens the duration of treatment, and reduces the burden on patients. It causes no pain to patients, and no complication after use has been reported. Therefore, it allows patients to receive treatment safely.
Surgical therapy
Surgical therapy
Coronary artery bypass is a surgical procedure that creates an alternate route around narrowed sections of coronary arteries to allow blood to flow.
A vessel is taken from the vein of the groin and connected to existing coronary arteries by detouring around coronary arteries from the aorta to ensure the blood flow to coronary arteries.
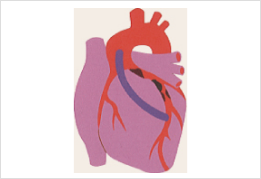
Vascular bypass implant is connected from the aorta to make a detour to avoid the lesion.
* The illustration is excerpted from MPC “Medicine and Health Illustrations.”
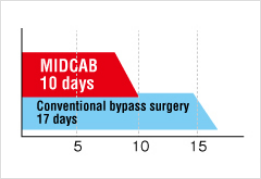
■Mean duration of hospitalization We perform minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypasses (MIDCAB) with minimal incision, without using a heart-lung machine.
【Cardiovascular Medicine】
052-362-5151052-353-9105
Kaikoukai Healthcare Corporation,Nagoya Kyoritsu Hospital
1-172 Hokke, Nakagawa-ku, Nagoya-shi, Aichi454-0933, JAPAN